In recent years, we have presented How to Spoof PDF Signatures and Shadow Attacks: Hiding and Replacing Content in Signed PDFs, which describe attacks on PDF signatures under various attack scenarios. The attacks focused on so-called approval signatures. However, in addition to signing PDFs, the PDF specification also specifies the certification of documents, also known as certification signatures.
To close this research gap, we performed an extensive analysis of the security of PDF certification. In doing so, we developed the Evil Annotation Attack (EAA), as well as the Sneaky Signature Attack (SSA). The attack idea exploits the flexibility of PDF certification, which allows signing or adding annotations to certified documents under different permission levels. Our practical evaluation shows that an attacker could change the visible content in 15 of 26 viewer applications by using EAA and in 8 applications using SSA by using PDF specification compliant exploits. We improved both attacks' stealthiness with applications' implementation issues and found only two applications secure to all attacks.
We responsibly disclosed all affected vendors. Together with the CERT-Bund (BSI), we supported the vendors in developing suitable countermeasures. The attacks are documented in CVE-2020-35931, CVE-2021-28545 and CVE-2021-28546.
PDF Structure and Basics
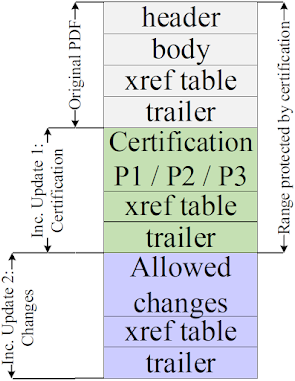
The figure on the left shows the file structure of a certified document. The first four building blocks are: header, body, xref table, and trailer. The header defines the version of the document, for example %PDF-2.0 for version 2.0. The body defines the content shown to the user after opening the file. The body contains different objects with different types. Common types are text, font, or image. There are dedicated objects that control the presentation of the PDF, such as Catalog, Pages, and Page. An example of an object is depicted in the listing below. The xref table contains the byte position of each object in the PDF. It allows PDF viewers to efficiently find all objects for processing. The trailer defines the byte position of the xref table and the root object of the PDF document's object tree. The root object is named Catalog and it is the first object to be processed, because it contains all relevant information about the document's structure.
The PDF specification additionally defines interactive elements that allow user input into the document. Such elements are separated in two categories: forms and annotations.
Forms. PDF forms allow user input in a predefined mask, such as a text field, a radio button, or a selection box. Facilities, such as the administration, usually use forms to create PDF documents with predefined areas which are intended to be filled out by users. The user input is, however, limited to the defined form fields and cannot change other content within the PDF.
Annotations. Annotations introduce a different method for a user input by allowing a user to put remarks in a PDF document like text highlighting, strikeouts, or sticky notes. Annotations are not limited to predefined places within the PDF and can be applied everywhere within the document.
Incremental Update
An Incremental Update introduces a possibility to extend a PDF by appending new information at the end of the file, see Inc. Update 1 in the figure above. In this way, the original document stays unmodified and a revision history of all document changes is kept. Each Incremental Update defines new objects, a new xref table, and a new trailer. An example of an Incremental Update is the inclusion of an certification, signature, annotation, or the filling out forms within a PDF.
User Interface (UI) Layers
The UI in many PDF viewing applications can be divided into three layers that are important for the verification of the certification.
UI-Layer 1: Top Bar Validation Status. UI-Layer 1 is usually displayed immediately after opening. Typical applications use a clearly visible bar on top of the PDF content. The status of the certification and signatures validation is provided as a text (e.g., valid/invalid), often combined with green, blue or red background colors, cf. figures in EAA and SSA sections.
UI-Layer 2: Detailed Validation and Information. UI-Layer 2 provides detailed information about the certification and the signatures applied to the PDF. It can be implemented by the viewer in numerous ways, but viewers typically do not show this information automatically once the PDF file is opened. Instead, it must be opened manually by clicking a certain button. For example, this button can be placed on the topbar (UI-Layer 1). Some viewers use sidebars which provide detailed information regarding the certified document, other use popup windows.
UI-Layer 3: PDF Annotations. UI-Layer 3 is another UI element that shows all PDF annotations. Typically, a sidebar is used for this purpose. This layer is of particular importance for certified documents, since for some documents, adding and changing PDF annotations is allowed. Without this layer, some annotations (e.g., text blocks) would be indistinguishable from regular PDF text content.
Difference between Signed and Certified Documents
Signed Documents
By signing a PDF document, a Signature object is created. This object contains the trusted public keys to verify the document, the signature value, the range of bytes that are protected by the signature, and a userfriendly information regarding the signer of the document. The Signature object is usually added to the PDF document by using an Incremental Update.
Certified Documents
Certifications have two main differences to signatures. First, each PDF can have only one certification and must be the first in the document. Second, certifications define permissions that allow certain changes to the certified document. As depicted in the table above, certifications define a more flexible way to handle Incremental Updates, and allowed Incremental Update do not lead to a warning. The certifier chooses between three different permission levels (P) to allow different modifications.
P1: No modifications on the document are allowed.
P2: Filling out forms, digitally signing the document are allowed, and instantiate page templates.
P3: In addition to P2, annotations are also allowed.
The allowed modifications are defined within the DocMDP Transformation parameter contained in the certification object. With respect to the integrity protection of the PDF, the PDF application must execute the following steps. First, it must verify if an Incremental Update was applied after the PDF was certified. Second, it must verify if the defined changes are legitimate according to the given permissions.
Evil Annotation Attack (EAA)
The idea of the Evil Annotation Attack (EAA) is to show arbitrary content in a certified document by abusing annotations for this purpose. Since P3 certified document allow to add annotations, EAA breaks the integrity of the certification.
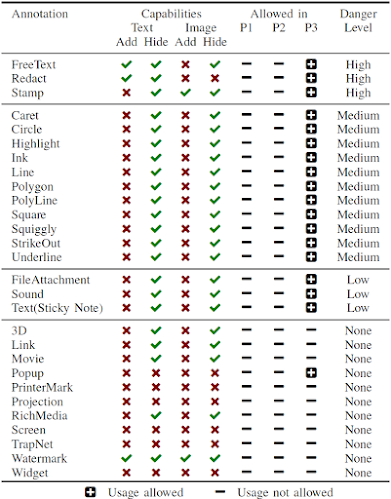
Evaluating Permission P3. According to the specification, the following changes in a certified document with P3 are allowed: 1) adding/removing/modifying annotations, 2) fillingout forms, 3) and signing the document. We started with an in-depth analysis of all annotations and their features. We evaluated 28 different annotations and classified these with respect to their capabilities and danger level. The results are depicted in the Table on the right side and will be further explained.
Danger Level of Annotations. We determined three annotations with a danger level high capable to hide and add text and images: FreeText, Redact, and Stamp. All three can be used to stealthily modify a certified document and inject malicious content. In addition, 11 out of 28 annotations are classified as medium since an attacker can hide content within the certified document. The danger level of the remaining annotations is classified as low or none since such annotations are either quite limited or not allowed in certified documents.
Attacking with Annotations. According to our attacker model, the attacker possesses a validly certified document allowing the insertion of annotations. To execute the attack, the attacker modifies a certified document by including the annotation with the malicious content at a position of attacker's choice. Then, the attacker sends the modified file to the victim who verifies the digital signature. The victim could detect the attack if it manually opens UI-Layer 3 or clicks on the annotation. However, none of the tested PDF applications opened UI-Layer 3 automatically. Additionally, the attacker can lock an annotation to disable clicking on it.
Improving the stealthiness of EAA
To improve the attack, we elaborated techniques to prevent the annotation's visualization, so that it does not appear in UI-Layer 3. Surprisingly, we found a generic and simple bypass that can be applied to all annotations. PDF viewers identify annotations by their specified /Subtype. This /Subtype is also used by the viewer to assign the various editing tools, such as a text editor for FreeText comments. If the value of /Subtype is either missing or set to an unspecified value, whereby both cases are not prohibited according to the specification, the PDF viewer is unable to assign the annotation. As depicted in the figure below, the annotation is not listed in UI-Layer 3. In summary, the annotation is indistinguishable from the original content.
Special Modifications
For some annotations, such as FreeText or Stamp, the editing tools of appropriate PDF applications can be easily used to completely design the visible content of a certified document. This is not the case for other annotations, which are classified as suitable for hiding text and images. The Underline annotation, for example, only creates a small line below the selected text. For hiding the text that is located below this line, the PDF object must be manually edited. By using a text editor, the thickness of the line can be adjusted within the annotation's appearance (parameter: /N) to hide the whole text. It is also possible to define the coordinates of an annotation to hide a particular area on a page. A special feature among the annotations is Redact. It allows new text to be placed over existing text. If the user moves the mouse over the text, the new text is displayed and hides the original text. To display this new text permanently, it is sufficient to redirect the object number (parameter: /N) to the object with the new text. Summarized, the specification does not restrict the size, color or characteristics of annotations and offers arbitrary possibilities to change the displayed content.
Sneaky Signature Attack (SSA)
The idea of the Sneaky Signature Attack (SSA) is to manipulate the appearance of arbitrary content within the PDF by adding overlaying signature elements to a PDF document that is certified at level P2.
Evaluating Permission P2. According to the specification, the following changes in a certified document with P2 are allowed: filling-out forms, and signing the document. We started the analysis of forms as depicted in the table on the right side and evaluated their capabilities.
Danger Level of Forms. According to our analysis, the danger level was none because the insertion of new form elements, customizing the font size and appearance, and removing form elements is prohibited. The only permitted change is on the value stored in the field. Thus, an attacker is not able to create forms which hide arbitrary content within the PDF document. Surprisingly, these restrictions are not valid for the signature field. By inserting a signature field, the signer can define the exact position of the field, and additionally its appearance and content. This flexibility is necessary since each new signature could contain the signer's information. The information can be a graphic, a text, or a combination of both. Nevertheless, the attacker can misuse the flexibility to stealthy manipulate the document and insert new content.
Attacking with Forms: SSA. The attacker modifies a certified document by including a signature field with the malicious content at a position of attacker's choice. The attacker then needs to sign the document, but he does not need to possess a trusted key. A self-signed certificate for SSA is sufficient. The only restriction is that the attacker needs to sign the document to insert the malicious signature field. This signing information can be seen by opening the PDF document and showing detailed information of the signature validation. In this case, the victim opening the file can get suspicious and refuse to accept the document, even though the certification is valid.
Improving the stealthiness of SSA
To circumvent this limitation, we found a bypass to hide this information in UI-Layer 2. Thus, the victim is not able to determine the attacker's manipulations (see the figure on the left side). Basically, we have three tasks to improve the attack execution: 1) hide the signature information in the signature panel on UI-Layer 2 , 2) skip the validation of attacker's signature, and 3) make the signature field read-only to make it indistinguishable from the text content. To solve all tasks, we need to adjust one object – the one responsible for the appearance of the signature. It contains three relevant parameters: /P, /V, and /Ff. The /P is a reference to the page where signature should be displayed. We found out that if this reference is not valid, the signature disappears from the signature panel on UI-Layer 2, but the malicious content is still shown on the page. A signature added to a PDF document is usually verified by processing its referenced signature data. If the stored cryptographic values are correct and the document is not manipulated within the signed area, the signature is technically valid. The /V parameter references the signature value which needs to be validated. We found out that if this reference is also invalid, the signature validation is skipped. Finally, we set the parameter /Ff to 1 which means that the content is read-only. If a certified document is opened in a common PDF application, signatures can only be added to free signature fields provided by the certifier. Adding empty signature fields is normally no longer possible within the application. However, the specification does not prohibit adding empty signature fields to a certified document. By using frameworks like Apache PDFBox, empty signature fields can be placed anywhere in the document and filled with arbitrary content.
Evaluation
We evaluated all 26 PDF applications on each of the three UI-Layers against EAA and SSA attacks. We used two different types of exploits for this purpose: 1) exploits that are compliant to the PDF specification and 2) exploits that improved the stealthiness of the attacks by abusing implementation flaws, for example, by parsing errors. We have evaluated the latest (at the time of evaluation) available versions of the applications on all supported desktop platforms: Windows, macOS, and Linux. The results are depicted in the table below.
Authors of this Post
Simon Rohlmann
Vladislav Mladenov
Christian Mainka
Jörg Schwenk
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to the CERT-Bund (BSI) team for the great support during the responsible disclosure. We also want to acknowledge the teams of the vendors which reacted to our report and fixed the vulnerable implementations.
Related posts